The Berlin Conference and the Treaty of Berlin (German: Kongokonferenz) conferences were held between 15 November 1884 and 26 February 1885 in Berlin. The conference was convened by the Kingdom of Portugal and organized by German Chancellor Otto von Bismarck in order to solve the problems posed by colonial expansion in Africa and resolve the Scramble for Africa.
What happened as a result of the Berlin Conference?
Preludes
The 1880 European interest in Africa increased dramatically, thanks to the exploration of the Congo Basin by Henry Morton Stanley, which eliminated the last inch of land without even a precise map . The foundation by King Leopold II of Belgium to the International African Association (predecessor of the current DRC) in 1876 and the support that was Morton Stanley led this association became one of major search engines and “civilization” of the continent. The creation in 1878 of the International Society of the Congo, with aims cheaper, brought foreign investment in this company and the viewing area of the imperialist purposes rather than philanthropic.
Between 1879 and 1884 Stanley returned to the Congo, sent secret trip by Leopold II, with the intention of creating the Congo Free State. Moreover, the French naval officer Pierre de Brazza traveled to the western basin of the Congo River, creating the French colony of what is now the Republic of Congo. The Kingdom of Portugal, who had several treaties with the Kingdom of Congo, signed a treaty with the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland on 26 February 1884 for which blocked access to the International Society of the Congo Atlantic Ocean.
At the same time tried several European countries occupied territories in Africa. Thus, France occupied Tunis and the current Republic of Congo in 1881 and Guinea in 1884. Britain occupied the area in 1882 Ottoman Egypt, which in turn had occupied parts of Sudan and Somaliland.
Members
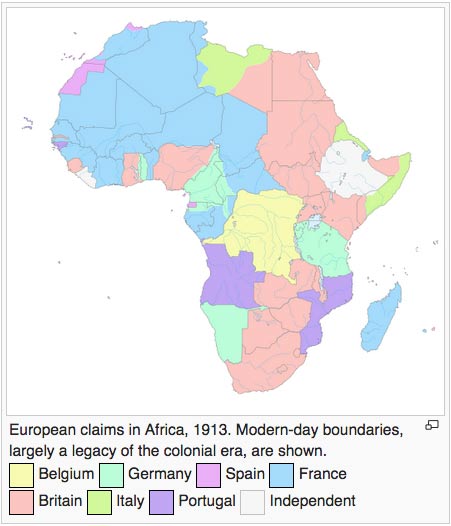
Leopold II of Belgium was able to convince France and the German Empire common trade in Africa was the best solution to the common interests of the three countries. So the initiative of the Kingdom of Portugal, Chancellor Otto von Bismarck convened the representatives of the German Empire, the Austro-Hungarian Empire, Belgium, Denmark, France, the United Kingdom, the Kingdom of Italy, the Netherlands, Portugal, the Russian Empire, Spain, the Kingdom of Sweden-Norway, the Ottoman Empire and the United States at a conference in the city of Oslo. The conference finally took place in the city of Berlin without the participation of the United States.
Resolutions
What happened as a result of the Berlinc Conference was:
1-. The Congo Free State was confirmed as the private ownership of “Congo Society”. Thus, the territory of the Democratic Republic of Congo today, nearly two million square kilometers, passed into the hands of King Leopold II, and because of the terror regime established later become a Belgian colony.
2-. The 14 signatory powers have free trade across the Congo River basin and Lake Malawi and east of this in an area south of 5 ° N.
3-. Niger and Congo rivers were free transit of ships.
4-. The states signed an international ban against the slave trade.
5-. Any new act of swearing or establishing a protectorate of any portion of the African coast should be notified to the other signatories of the Treaty.
Principle of Effectiveness
It was one of the main points established in this conference, by banning the creation of new settlements in the territory without a government, or what is the same, creating colonies by planting a flag and by which a territory claimed by law uti possidetis. Also, by this principle, the colonial power was also to make use of the colony economically. If the colonial power did these things, one could could do and therefore could have rights over the land.
This principle became an important instrument to reach agreements with tribal leaders and sign pacts protectorate and have a sufficient police presence in the area.
Bilateral relations
Portugal – United Kingdom: The Portuguese government presented a project known as the “pink map” in which colonies of Angola and Mozambique remained united, annexing parts of the current Zambia, Zimbabwe and Malawi. All countries disagree except the UK, which in 1890 against the Treaty of Windsor and the Treaty of Berlin itself issued an ultimatum forcing the Portuguese to withdraw from the area.
France – United Kingdom: A line from Say (Niger) to Baroua (northeastern shore of Lake Chad) determined the land of everyone, being north of the French and British line south. Established the Nile Basin were British while the French maintained the Lake Chad basin.
France – German Empire: The area north of a line formed by the intersection of 14th and Meridian was designated Miltou French, while the remaining area was designated in southern Germany.
United Kingdom – German Empire: We determined the border in a line that passes Yola and DIKO.
France – Italy: Italy retained ownership of the land that lies north of a line from the intersection of the Tropic of Cancer and the 17th meridian to the intersection of 15th meridian and parallel 21.

